Mornsun: Applications of AC-DC Converters
To generate DC voltage, switching mode power supplies (SMPS) immediately alter and filter the AC power input. A high-frequency transformer or inductor is used to change the DC voltage into an AC current at switching frequencies between 10 kilohertz and 1 megahertz, using an electronic switching circuit. Transformers and filter capacitors can be made smaller, lighter, and cheaper because of the increased switching frequencies. In order to get a consistent DC voltage, the high-frequency AC is filtered and modified after passing through an inductor or transformer.
To generate DC voltage, switching mode power supplies (SMPS) immediately alter and filter the AC power input. The DC voltage is then converted to high-frequency AC current using an electronic switching circuit, typically operating between 10 kHz and 1 MHz. This is accomplished by allowing the DC voltage to flow through a high-frequency transformer or inductor. Transformers and filter capacitors can be made smaller, lighter, and cheaper because of the increased switching frequencies. High-frequency alternating current is regulated and filtered after passing through an inductor or transformer to generate a clean direct current. Different topologies can be employed for the optimal equalization depending on the power range, input voltage range, output voltage, space limits, and efficiency goals.
As part of power factor correction (PFC), the offline converter’s input filter capacitor is placed in series with the rectifier bridge’s output terminals, and a prevoltage regulator is placed between them. This allows the supply current to be sinusoidal rather than asymmetrical with respect to the line voltage. This method allows for the achievement of both a high power (PF) factor value (” 0.9 “) and a low total harmonic distortion (” THD “) value (” 10% “) in the input current. The boost structure is commonly employed as it offers numerous benefits.
The primary function of a half-bridge CONVERTER, an AC-DC power supply, is to alleviate the voltage load on the system’s primary switches. The downlink converter requires a steady high voltage bus, which is typically supplied by the power factor correction (PFC) front stage. The accompanying circuit diagram will assist in making the best possible product selections.
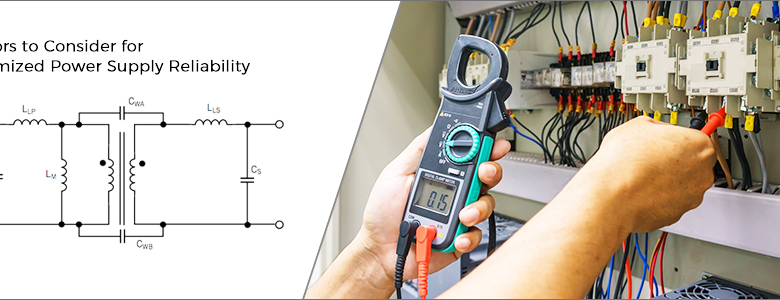
Power conversion from alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) is the primary application of the flyback converter. This converter is a transformer-based current-isolated step-up converter, rather than an inductor-based one. By connecting the transformer coils in the positive direction, a positive output can be obtained. A proper product selection can be aided by the following circuit diagram.
When converting DC-DC with a low input voltage, a push-pull converter is the way to go. The accompanying circuit diagram will assist in making the best possible product selections.
The forward converter, a type of current isolation step-down converter typically used in ac to dc converter power supplies. If you need a converter with a greater output voltage than a flyback circuit can provide, Mornsun’s product is the one to choose. It is true that the energy efficiency of forward converter is greater than that of flyback converter. With any luck, the following circuit diagram will guide you in making the best possible product choice.



